2. VS Code – Code Runner Extensions for PowerShell.
3. VS Code – Terminal session.
VS Code – Terminal session
Max Trinidad – The PowerShell Front
A little of everything about PowerShell!!!
Hum! I just found out that in SQL Server 2014 (SP2 installed), while migrating from SQL Server 2005, one of my PowerShell script (I’ve been using for a long time) that uses SMO to truncate tables. But, when running it against a SQL Server 2014 database, I’m getting an error:
“..this property is not available on SQL Server 2014.”
For mi surprise, I ran the same PowerShell script against SQL Server 2016 and it works fine.
Here’s a sample function that does a Truncate to all my tables in a database:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Clear-DatabaseTable
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[string]$SQLServerInstanceName,
[string]$SQLServerDatabasename
)
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName(“Microsoft.SQLServer.Smo”) | Out-Null;
$SQLSrvObj = new-object(‘Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server’) $SQLServerInstanceName;
$tables = $SQLSrvObj.Databases[$SQLServerDatabaseName].tables;
## Database tables rowcounts before truncate:
$tables | Select @{ Label = “TruncatedTable”; Expression = { $_.Schema + “.” + $_.Name }; }, `
@{ Label = “PrevRowCount”; Expression = { $_.rowcount }; } | FT -auto
$ReadThis = `
“**********************************************************************`r`n ” `
+ “Do you really want to Truncate all tables in $SourcedbName ? Y/N `r`n” `
+ “**********************************************************************`r`n “;
$Cont = Read-Host $ReadThis;
[console]::ResetColor();
if ($Cont.ToUpper() -eq ‘Y’)
{
foreach ($t in $tables)
{
Write-Verbose “Truncating Table $($t)” -Verbose;
$t.TruncateData();
};
};
};
[/sourcecode]
Load this function into you session and then run the following command:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
Clear-DatabaseTable -SQLServerInstanceName ‘MTRINIDADLT2\MSSQL2K16A’ `
-SQLServerDatabasename ‘devMaxTest’;
[/sourcecode]
The results against SQL Server 2016 were successful:
But, when running against SQL Server 2014, I get the error:
I logged this issue under SQL Server UserVoice: https://manage.uservoice.com/forums/108777-database-manager-for-sql-azure-feature-suggestions/suggestions/16286755-sql-server-2014-is-missing-smo-truncatedata-met
Please Vote on it!
I recently went back to try using VS Code. Now that I’m fully invested with PowerShell Open Source in Ubuntu Linux 16.04.1 Desktop. During trails and errors I found at least three ways to execute PowerShell:
1. VS Code – PowerShell Extension and Debug feature.
2. VS Code – Code Runner Extensions for PowerShell.
3. VS Code – Terminal session.
First, we need to add a couple of extensions:
1. PowerShell
2. Code Runner
In below image, we are installing Python Extensions. In Linux, having Python installed will be of great benefit.
These are a most-to-have extensions to work with PowerShell. We are going to use the Debug feature.
First, we are going to use VS Code debug option to run PowerShell Out-Of-The-Box. This way we can be use debug to execute and step thru the PowerShell script code.
Open the folder were the scripts are going to be stored. The first time using the Debug it will ask to create the “launch.json” which is needed in order to execute and debug the script. Accept the default values as you can change them later if needed.
By the default, in Windows OS, it will execute Windows PowerShell ver 5.x. In Linux, it will run the PowerShell Open Source. Keep in mind, I’m on a Linux system.
Next, is to create a new “settings.json” file, go to VS Code menu click on “File | Preferences | User Settings“. In order to execute PowerShell Open Source, which is in a different folder, we need to create a “settings.json” file with the following code:
So, you’ll ended up with two *.json files in your script folder. Then, you can customized these file to work with your script code when it gets debug.
Bonus Note: On a Windows System, if you want to customize VS Code to use PowerShell v6.0.0-alpha.x, just add the following line in the “settings.json” file:
Next blog post, I’m going to cover “VS Code – Code Runner extension“
Yes! Now, PowerShell will be available CrossPlatform to help any system automation need. As a Linux newbie, I’m excited about this announcement.
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/mt173057.aspx
So, if you have Linux Systems such as Ubuntu, CentOS, and, even for Mac OS X 10.11.
Check the link: https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell
Just go and get it. But, keep in mind, this is a work in progress.
This is PowerShell Core only, Alpha Version 6.0.0.9 and there’s a lot of work to do. Bugs and feedback are been submitted as the community are contributing for it success.
This version is also available for Windows 10 / Server 2016 and Windows 8.1 / Server 2012 R2. You can have it side-by-side with the current version of PowerShell.
Just follow the instruction provided in the GitHub PowerShell page, look for your Linux version, and follow the link provided for downloading installation package: https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/blob/master/docs/installation/linux.md#ubuntu-1604
In my case, I took the setup for Ubuntu 16.04:
After the installation is completed then you are ready to run PowerShell from any of the Linux Terminal applications.
So, a word of caution! if you try to use a cmdlet from Windows to access a Linux system, your Windows PowerShell session will crash.
Just a reminder! Here are some PowerShell resource link to save.
Microsoft just recently announce the PowerShell “Windows Management Framework 5.1 Preview“. Check the PowerShell Team Blog:
*note: Keep in mind. WMF 5.1 Preview is not supported in production environments.
Windows PowerShell Home Page
https://msdn.microsoft.com/powershell
Windows Management Framework 5.1 Preview
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53347
Don’t forget to check WMF 5.1 Release Notes
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/wmf/5.1/release-notes
PowerShell for Visual Studio Code
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemname=ms-vscode.powershell
SAPIEN Technologies ‘PowerShell Studio 2016’ – The premier editor and tool-making environment for Windows PowerShell
https://www.sapien.com/software/powershell_studio
SQL Server with Windows PowerShell
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt740629.aspx
SQL PowerShell: July 2016 update (SSMS only)
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/dataplatforminsider/2016/06/30/sql-powershell-july-2016-update/
Get SSMS July 2016 download is at https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt238290.aspx
Go and keep learning about PowerShell!!
Go and get it. Of course, No SQLServer PowerShell update on this hotfix. But you’ll need this update.
Read more on this link for more information: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt238290.aspx
If you are still interested of see what’s new in this July Edition of SSMS, check the following Microsoft Blog site:
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/dataplatforminsider/2016/06/30/sql-powershell-july-2016-update/
On previous blog we have collect some data and built our .NET PowerShell object which is going to be loaded into our SQL Server.
In this final section we are completing the process of loading the data into SQL Server. We need to make sure we got our Database and table previously created and ready to receive our data.
For this process we’ll need to create 3 functions:
1. ConnectTo-SQLServer
2. Load-LogRecord
3. Process-PSObjectToSQL
Of course we could do everything in one long script file. But, by breaking out into it will make it much easier to handle and maintain.
In order to connect to SQL Server, we’ll be using straight SMO classes to load the data. Also, we’ll integrate some basic error catching using “try-catch” code block structure.
I’m keeping the functions in a basic level hardcoding some the PSObject variables instead of using parameter names. Keep in mind, the use of parameter name(s) in a function brings a lot flexibility and function reusability.
Function – ConnectTo-SQLServer
Using SMO with a few lines of code we connect to a SQL Server engine. Here’s the basic script code to will allow us to initiate a connection to SQL Server:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function ConnectTo-SQLServer
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param ()
## – Select SQLServer:
$global:SQLServerInstanceName = "MTRINIDADLT2";
$global:SQLServerDatabaseName = "LogEntries";
$global:logServerName = "tcgsvvm04";
�
## – Loading SMO .NET Assembly: (Required)
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SQLServer.Smo") | Out-Null;
�
## – Connecting to SQL Server (Windows Authentication) and building you table object:
$global:SQLSvrObj = new-object(‘Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server’) $SQLServerInstanceName;
$global:SQLSvrObj.ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout = 0;
};
[/sourcecode]
You will notice the use the of “$global:variablename” with some of the variable objects created. This way we won’t loose the value stored in my PSObject(s) like “$global:SQLSvrObj” and have it available to other PowerShell function(s).
Function – Load-logRecord
This function show a Kind-Of template for using T-SQL insert statement to an existing table and at the same time subtitute the PSObject variable(s) constructing full qualify database table name. We construct the T-SQL Insert string and then to execute the query using SMO database *method “.ExecuteNonQuery($global:insertqry)”.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Load-logRecord
{
CmdletBinding()]
Param ()
$global:insertQry = @"
INSERT INTO [$($global:SQLServerDatabaseName)].[dbo].[$($global:logServerName)_Log]
([Column1]
, [Column2]
, [Column3]
, [Column4]
, [Column5]
, [Column6]
, [Column7]
, [Column8]
, [Column9]
, [Column10]
, [Column11]
, [Column12]
, [Column13]
, [Column14]
, [Column15]
, [ServerName])
VALUES
( ‘$($global:l.Column1)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column2)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column3)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column4)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column5)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column6)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column7)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column8)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column9)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column10)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column11)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column12)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column13)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column14)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column15)’
, ‘$($global:LogServerName)’)
GO
"@;
 $global:SQLSvrObj.Databases["Master"].ExecuteNonQuery($global:insertQry);
};
[/sourcecode]
*Note: Keep in mind, by saving the PSObject variable with a $global: scope, you will access to its value after the function has been executed or the value will be dispose (null).
Function – Process-PSObjectToSQL
This is the heart of loading the data. Here we use both previous functions: 1. ConnectTo-SQLServer and
2. Load-LogRecord.
This a simple code block using the ForEach() block to read thru the PSObject variable to load the data into SQL Server. All accomplished with a few code block.
Now, here’s where we’ll include our error catching code block in case we encounter any data load issue during this process.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Process-PSObjectToSQL
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[array]$SQLDataObj
)
## Start process
Try
{
ConnectTo-SQLServer;
$global:cnt = 0
Write-Verbose "Start loading Data to SQL Server" -Verbose;
foreach ($global:l in $SQLDataObj)
{
Load-logRecord;
$global:cnt++;
}
}
catch
{
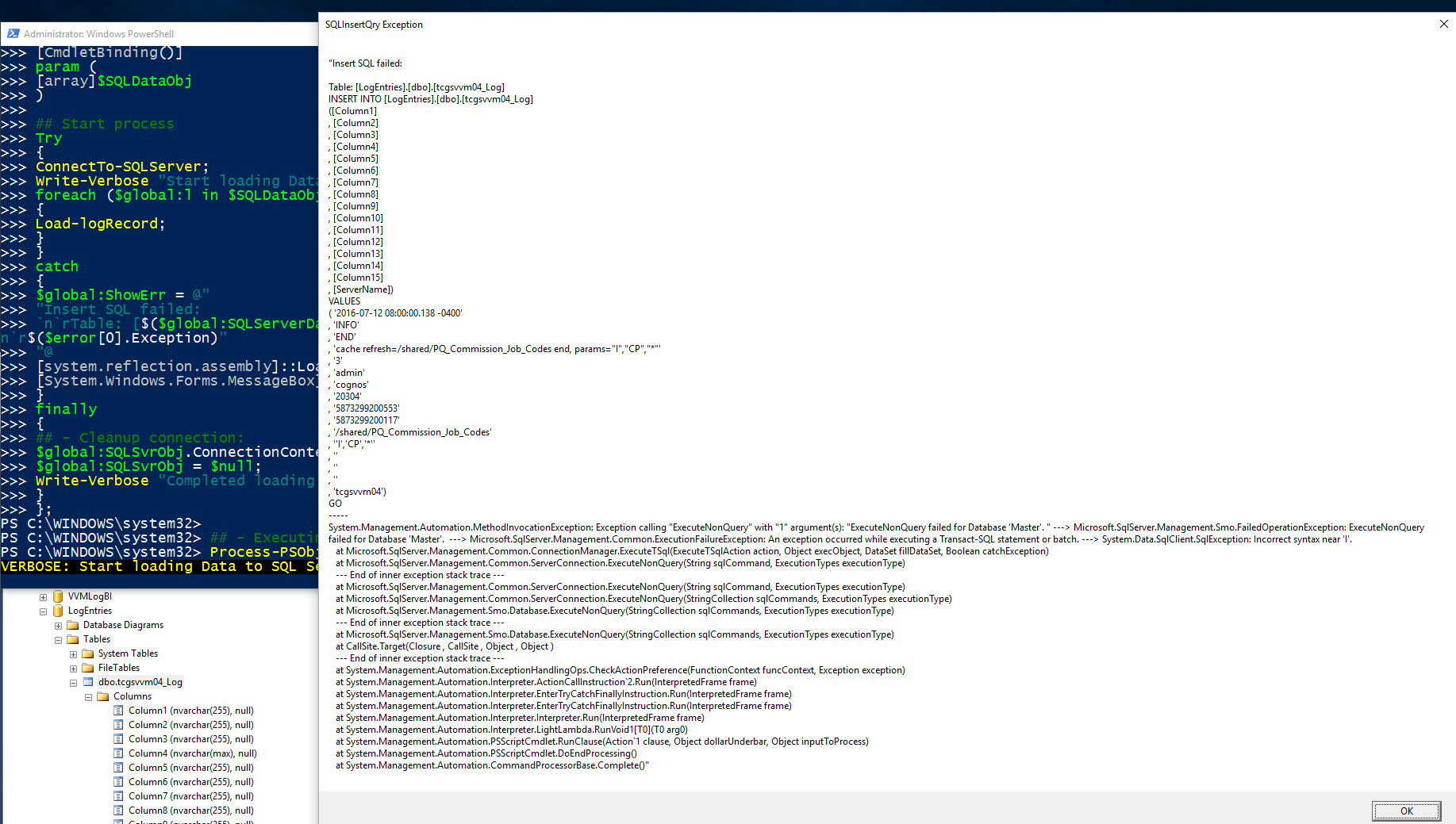
$global:ShowErr = @"
Insert SQL failed: Record #[ $($global:cnt) ]`n`r—–
Table: [$($global:SQLServerDatabaseName)].[dbo].[$($global:logServerName)_Log]`n`r—–
$($global:insertQry)`n`r—–`n`r$($error[0].Exception)
"@
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("System.Windows.Forms") | Out-Null;
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show("$global:ShowErr", "SQLInsertQry Exception") | Out-Null;
�
$errfound = $true
}
finally
{
## – Cleanup connection:�
$global:SQLSvrObj.ConnectionContext.Disconnect();
$global:SQLSvrObj = $null;
if ($errfound -eq $true)
{
Write-Verbose "Failure loading Data to SQL Server!" -Verbose;
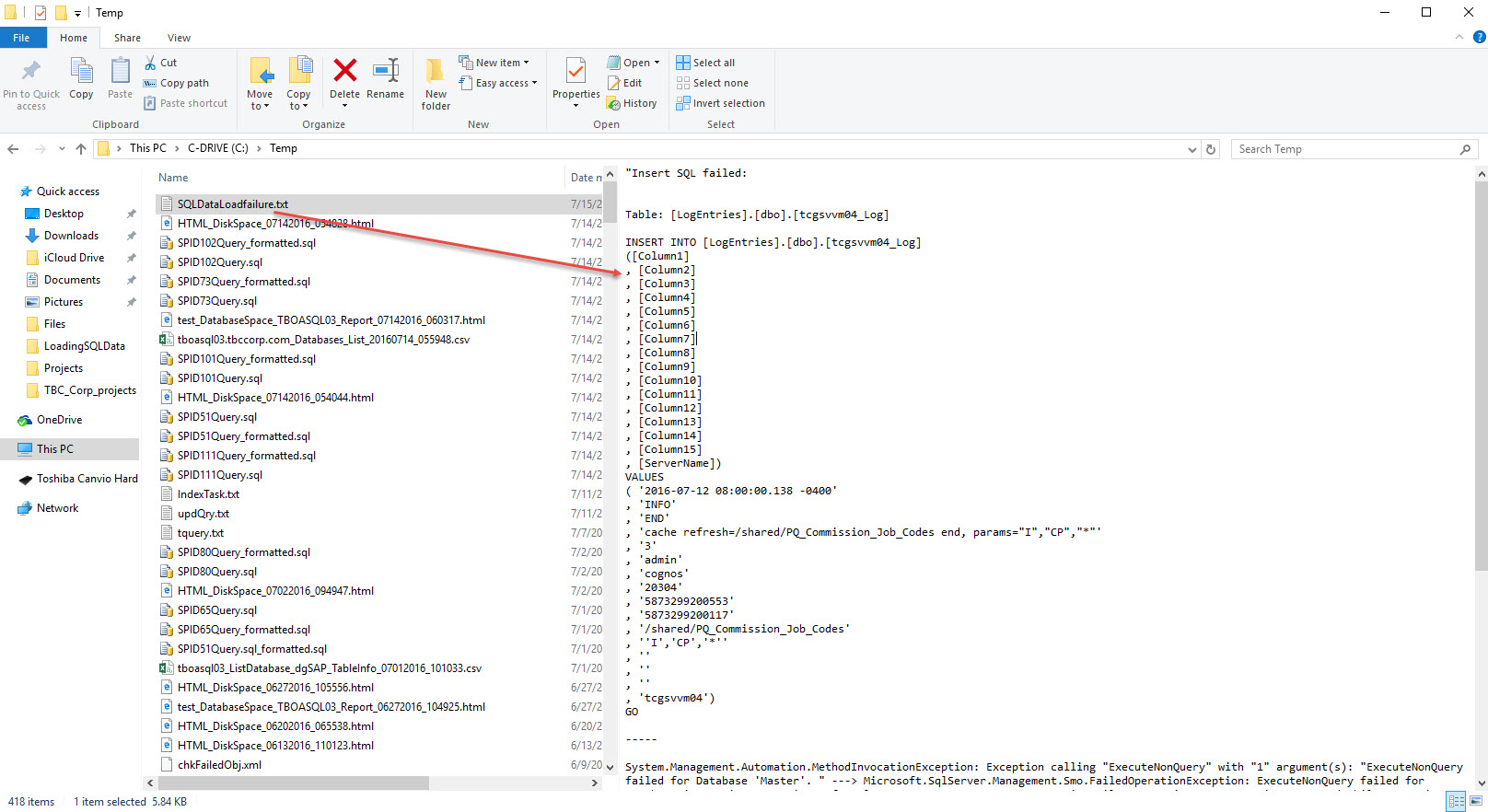
$global:ShowErr | Out-File -FilePath c:\Temp\SQLDataLoadfailure.txt;
Invoke-Item c:\Temp\SQLDataLoadfailure.txt;
}else{
Write-Verbose "Completed loading Data to SQL Server" -Verbose;
}
}
};
[/sourcecode]
This function has a ParameterName $SQLDataObj. This will take the previously created $SQLData PSObject to be loaded to SQL Server.
In Error catching code block, the try{..} contains all the logic code to process the data. Then, the catch{..} has a custom string with enough information to trouble the issue the process may have encountered, such as: Fully qualified Database name, Insert Query T-SQL script, and the actual Exception error message.
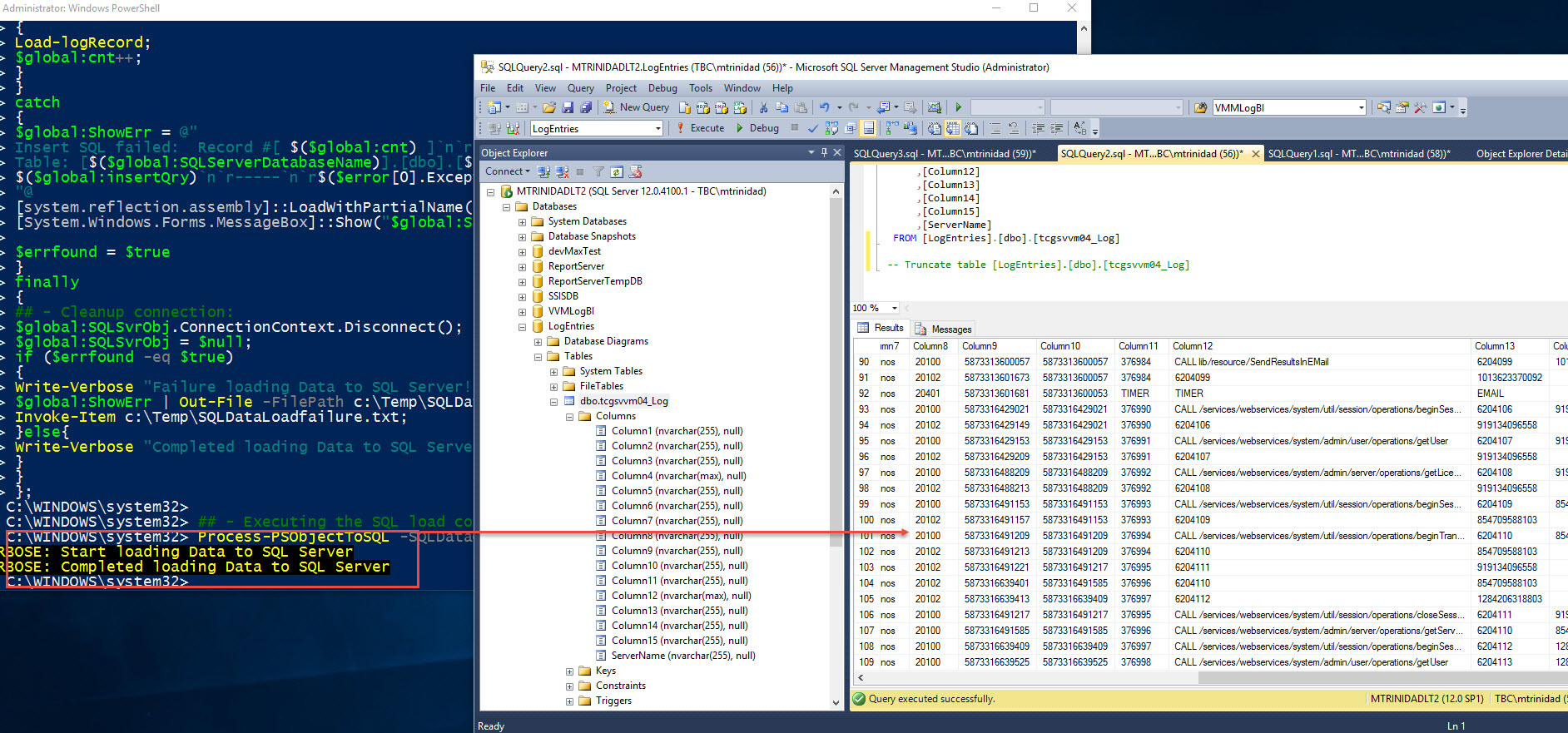
At the end of the process, error or not, the finally{..} block will always execute the code. In this case, to disconnect and cleanup the connection to SQL Server.
Executing the process
After all the previous functions has been loaded, just type the following one-liner:
Process-PSObjectToSQL -SQLDataObj $SQLData;
This sample script code can serve as a startup Template to load data into SQL Server.
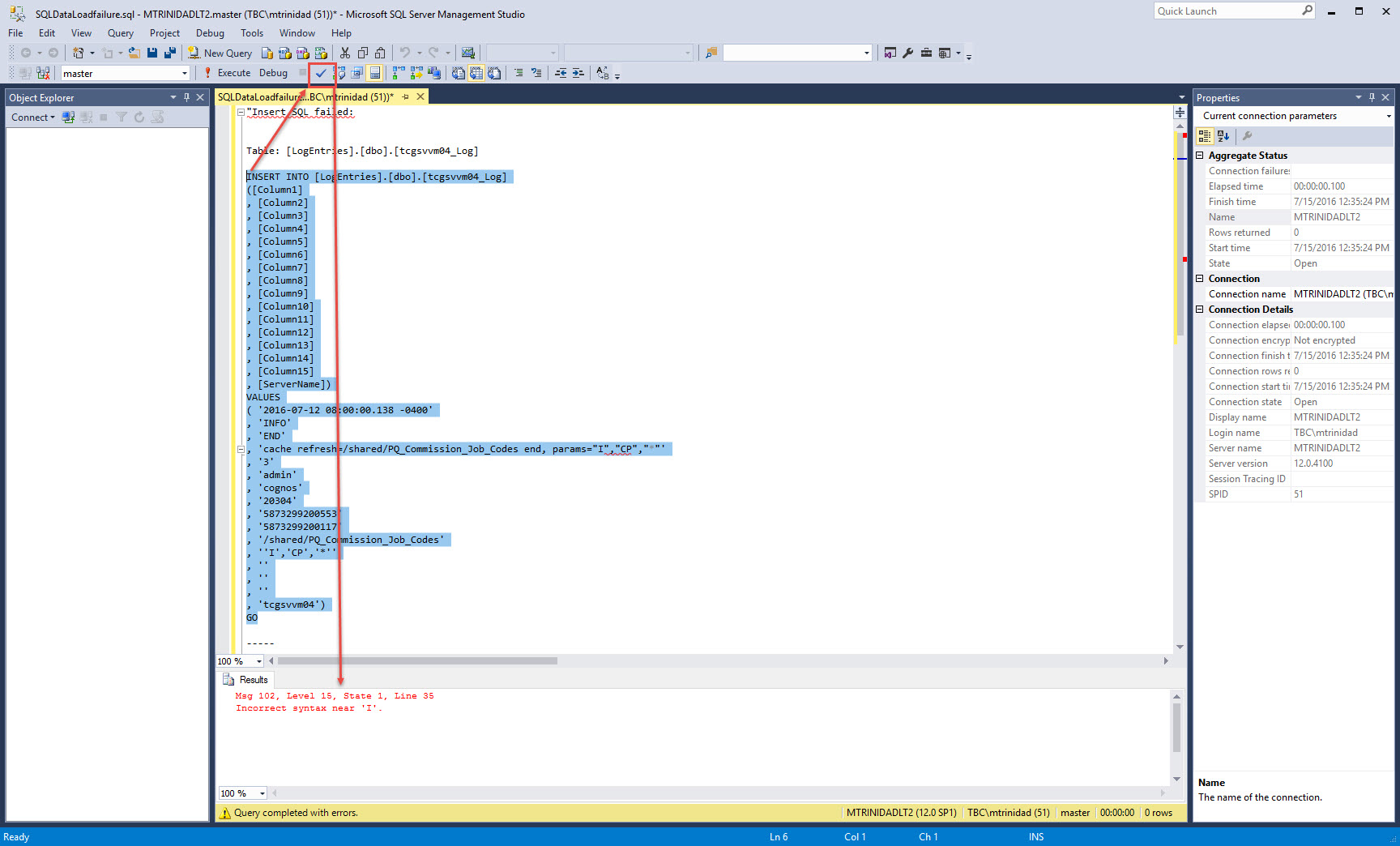
This sample SQL data load will fail. Here’s when the Try/Catch/Finally will work for you in trapping what went wrong. Adding the necessary code to provide that additional information to troubleshoot and fix the problem.
Be Creative! Check out the results.
Happy PowerShell!
It’s a busy and a good time to learn some PowerShell.
1. Where: Florida PowerShell User Group Monthly meeting, Date: Thursday, May 26th at 6:30pm. Online
Topic: The Essential PowerShell on Error Trapping.
Description:
Do you to learn how to trap and document error while running PowerShell scripts? This session will cover the use and how to trap errors in your PowerShell script. We’ll be creating simple script providing some scenarios in trapping errors. At the same time, we are going to end up creating an error report.
Register at Eventbrite: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/florida-powershell-user-group-monthly-meeting-may-2016-tickets-25454080841
2. Where: Idera Geek Synch, Date: Wednesday, June 1st at 12:00pm – 01:00pm, Online
Topic: The Essential PowerShell Tools for the DBA Administrator.
Description: I will covers the some of my favorite PowerShell tools I uses on a regular basis. In this session I will be showing some available tools the DBA can use along with PowerShell. I’ll be integrating Visual Studio with PowerShell and at the same time using IDERA’s PowerShellPlus editor. At the end, we’ll build an SSIS package solution to execute our PowerShell script. It will be pack with interesting thing to do as well as help you accomplish your automation tasks.
Register at: https://www.idera.com/events/geeksync
3. Where: IT Pro Camp Jacksonville. Date: Saturday, June 11th All Day Event. (In Person)
Topic: The Essentials of Tackling PowerShell Basic Functions
Description: I will demonstrate creating a PowerShell function from a one-liner and/or an existing script file in its basic form. This is an example of the script evolution which you’ll experience while building you PowerShell skills.
Register at: http://itprocamp.com/
4. Where: SQLSaturday South Florida. Date: Saturday, June 18th, All Day Event. (In Person)
Topic: SSIS – Integrating PowerShell in a ScriptTask component
Description: This session will demostrate how you can reuse a PowerShell script in SSIS “Script Task” component as part on a ETL flow. I’ll be showing some basic .NET Script code in both C# and VB. I’ll be adding some useful tips when re-using existing Powershell code. Integrating different .NET technologies in a SSIS package: C#, VB.NET, XML, and PowerShell.
Register at: http://www.sqlsaturday.com/524/EventHome.aspx
Come and say Hi!