Now that we got the connection to the server there are a couple of lines we could include to avoid connection timeout during execution of our T-SQL script using SMO with PowerShell. So, in this blog will be covering executing a T-SQL script and viewing its results.
The *T-SQL script will build me table with data statistics about my selected Database indexes need to either Reorganize, or Rebuild.
*Note: The following T-SQL script modified from its original “Index optimization – REBUILD vs. REORGANIZE” by Author Sarjen Haque. It can be found at http://sqltouch.blogspot.com/2013/07/index-optimization-rebuild-and.html
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
$TSQLqry1 = @"
if object_id(‘$($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]’) is not null
begin
Drop Table $($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList];
end
select
‘$($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]’ as [IdxFragStatDatabase] ,
‘$($DatabaseName)’ as [IdxFragStatOnDatabase] ,
object_name(o.object_id) as [table_name] ,
schema_name(o.schema_id) as [schema_name] ,
i.name as [index_name] ,
i.type_desc as [index_type] ,
dmv.page_count as [Page_Count] ,
dmv.fragment_count as Fragment_Count,
round(dmv.avg_fragment_size_in_pages, 2, 2) as [avg_fragment_size_in_pages] ,
round(dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent, 2, 2) as [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] ,
case when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent <= 5 then ‘RELAX’
when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent <= 30 then ‘REORGANIZE’ when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 30 then ‘REBUILD’
end as [action],
getdate() as [RunOnDate]
into $($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]
from sys.partitions as p with ( readpast )
inner join sys.indexes as i with ( readpast ) on i.object_id = p.object_id
and i.index_id = p.index_id
inner join sys.objects as o with ( readpast ) on o.object_id = i.object_id
inner join sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(db_id(), null, null, null, N’LIMITED’) dmv
on dmv.OBJECT_ID = i.object_id and dmv.index_id = i.index_id
and dmv.partition_number = p.partition_number
where objectproperty(p.object_id, ‘ISMSShipped’) = 0
and (i.name is not Null and i.type_desc <> ‘HEAP’)
order by [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] DESC,
[table_name],
[index_name]
"@;
[/sourcecode]
Notice that PowerShell will substitute the values for $($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList] within the Here-String @” .. “@. It’s important to notice when using Here-String TABS are not allow at the end of ‘@”;’ or you’ll get an error.
Back to the connection section. We need to include the following just after the ‘$MySQL = New-Object $MySQL = new-object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server …‘:
$MySQL.ConnectionContext.ConnectTimeout = 21600; (This is an example (optional) set to 21600 sec = 6hrs)
$MySQL.ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout = 0; (This is an example set to 0 for no timeout when running T-SQL queries)
Here’s the sample for the code placement:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## – Connect and Execute T-SQL script:
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SQLServer.Smo") | Out-Null;
$MySQL = new-object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server $SQLServerInstanceName;
#$MySQL.ConnectionContext.ConnectTimeout = 21600; #Optional#
$MySQL.ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout = 0;
[/sourcecode]
If you don’t use the ‘ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout’ you’ll get a timeout error after 10 minutes of execution.
Now, we proceed to create our variables use for the T-SQL script:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
[string] $SQLServerInstanceName = ‘.’
[string] $DatabaseName = ‘AdventureWorks2014’
[string] $tblSchema = ‘dbo’
[string] $IdxStatDatabase = ‘devMaxTest’
[/sourcecode]
The purpose of the $IdxStatDatabase is to redirect the data index stat report to another Database. Then, we use the following line to execute our T-SQL script using SMO with PowerShell.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
$r = ($MySQL.Databases[$DatabaseName]).ExecuteWithResults($TSQLqry1);
[/sourcecode]
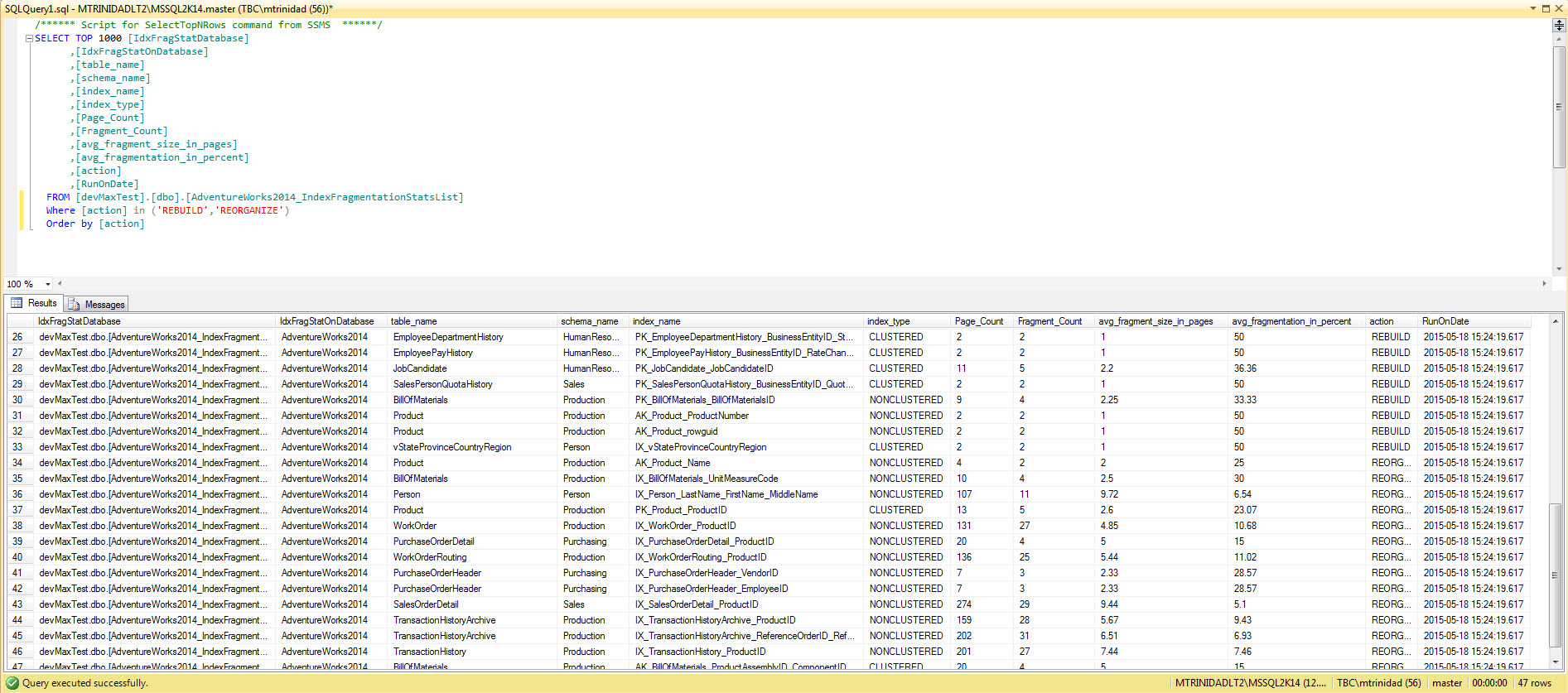
After the PowerShell script execute, open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), go to the database where the index stat data is stored, and query the table to view results.
This report will help you identify those indexes that need to be taken care off.
Full sample script below:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## – Set variables for T-SQL script:
$SQLServerInstanceName = ‘.’;
$DatabaseName = "AdventureWorks2014";
$tblSchema = "dbo";
$IdxStatDatabase = "devMaxTest";
## – Build the T-SQL script for execution:
$TSQLqry1 = @"
if object_id(‘$($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]’) is not null
begin
Drop Table $($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList];
end
select
‘$($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]’ as [IdxFragStatDatabase] ,
‘$($DatabaseName)’ as [IdxFragStatOnDatabase] ,
object_name(o.object_id) as [table_name] ,
schema_name(o.schema_id) as [schema_name] ,
i.name as [index_name] ,
i.type_desc as [index_type] ,
dmv.page_count as [Page_Count] ,
dmv.fragment_count as Fragment_Count,
round(dmv.avg_fragment_size_in_pages, 2, 2) as [avg_fragment_size_in_pages] ,
round(dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent, 2, 2) as [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] ,
case when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent <= 5 then ‘RELAX’
when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent <= 30 then ‘REORGANIZE’ when dmv.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 30 then ‘REBUILD’
end as [action],
getdate() as [RunOnDate]
into $($IdxStatDatabase).$($tblSchema).[$($DatabaseName)_IndexFragmentationStatsList]
from sys.partitions as p with ( readpast )
inner join sys.indexes as i with ( readpast ) on i.object_id = p.object_id
and i.index_id = p.index_id
inner join sys.objects as o with ( readpast ) on o.object_id = i.object_id
inner join sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(db_id(), null, null, null, N’LIMITED’) dmv
on dmv.OBJECT_ID = i.object_id and dmv.index_id = i.index_id
and dmv.partition_number = p.partition_number
where objectproperty(p.object_id, ‘ISMSShipped’) = 0
and (i.name is not Null and i.type_desc <> ‘HEAP’)
order by [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] DESC,
[table_name],
[index_name]
"@;
## – Connect, set timeout values:
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SQLServer.Smo") | Out-Null;
$MySQL = new-object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server $SQLServerInstanceName;
#$MySQL.ConnectionContext.ConnectTimeout = 21600; #Optional#
$MySQL.ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout = 0;
## – Execute T-SQL script:
$r = ($MySQL.Databases[$DatabaseName]).ExecuteWithResults($TSQLqry1);
Write-Host "End of Script";
[/sourcecode]